MUKHAMEDZHANOV MURAT
Corresponding Member of the National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Doctor of Geological and Mineralogical Sciences, Scientist, Specialist in the field of Hydrogeology
The purpose of the project:
Scientific substantiation and identification of promising areas for artificial replenishment of groundwater reserves in water-deficient small-hill districts of Central Kazakhstan for the purpose of water supply to populated areas, industrial enterprises and pasture irrigation, development of typical technological schemes for artificial replenishment applicable to various physical-geographical, geological-geomorphological and hydrogeological conditions of the region, zoning of the territory according to the conditions for replenishment of groundwater reserves.
Project objectives:
1) collection, generalization and analysis of geological and hydrogeological archive data to assess the level of MAR issues in the region, to establish patterns of groundwater formation and the possibility of MAR in the hydrogeological structures and aquifers of the region, the presence of water for replenishment, the state of drinking water supply to settlements and industrial enterprises;
2) interpretation of aerial and space images and remote sensing results to identify promising areas for the creation of MAR typical technological schemes and to establish patterns of groundwater distribution and formation;
3) study of small-hill districts of Central Kazakhstan for the possibility of constructing water intake and irrigation structures for MAR;
4) conducting field work (reconnaissance routes, inspection of water points, water sampling, etc.) in order to study the hydrogeological and geoecological state, select a site for MAR;study of the most promising areas identified during the interpretation of the results of remote sensing and space images;
5) based on the results of field work, concepts will be developed and specialized hydrogeological maps of small-hill districts of Central Kazakhstan will be compiled at a scale of 1:1,000,000 – 1:500,000 with zoning of the region's territory according to the conditions of the MAR and large-scale hydrogeological maps of promising areas, which will allow identifying specific areas for the MAR;
6) development of practical recommendations for the creation of standard technological schemes of the IVZPV for water supply of settlements and industrial enterprises applicable to various physical-geographical, geological-geomorphological and hydrogeological conditions of the region;
7) development of proposals for the phased development of groundwater through the construction of underground reservoirs;
8) development of possible technical solutions.
THE RELEVANCE OF THE PROJECT: -2024 ye.
Uneven distribution of water resources, the steady growth of water consumption, significant pollution of surface water, the intensification of groundwater withdrawal in economically developed areas, the existing shortage of fresh water of drinking quality and other factors necessitate the use of methods for artificial replenishment and regulation of groundwater reserves. In areas where groundwater is an important component of the water supply system, and the variability of precipitation does not allow for a sufficient replenishment of groundwater reserves in aquifers in a natural way, it is necessary to use technologies for artificial replenishment of these reserves due to atmospheric precipitation or surface water resources that ensure their maintenance.
THE RELEVANCE OF THE PROJECT: -2025 ye.
1. Based on the interpretation of satellite images, it was established that the nodes of highest lineament density correspond to zones of tectonic fracturing in the water-bearing rocks. This helped to determine groundwater flow directions and identify perspective areas for aquifer studies. A comprehensive hydrogeological and lineament-geodynamic analysis of remote sensing data, taking into account fracturing, allowed us to predict new perspective zones, grouped according to key hydrogeological parameters. The main perspective areas are confined to the alluvial valleys of the Nura, Atasu, Sarysu, Zhaman-Kon, Zhaksy-Kon, and Terenbutak rivers and their tributaries, as well as to Devonian-Carboniferous carbonate structures, Paleozoic deposits, and intrusive massifs.
2. Field reconnaissance surveys were conducted in the Zhanaarka and Shetsky districts of the Ulytau region and certain districts of the Akmola region. The total length of the survey routes was 5,000 km.
Twelve promising sites for Managed aquifer recharge were identified. The field and paper work yielded the following analytical indicators for each site:
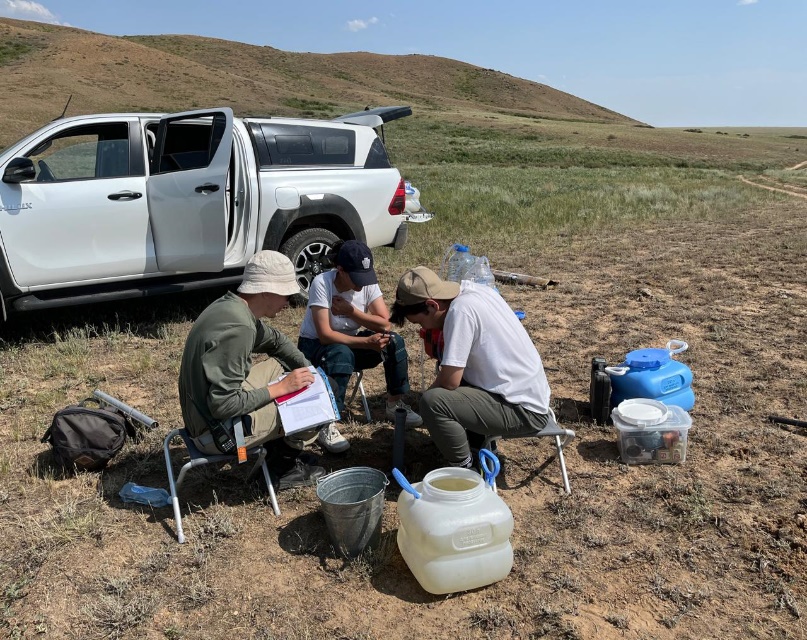
- the composition of aquifers in the vadose zone and the groundwater table were determined using borehole drilling;
- the chemical composition of groundwater samples collected at the sites was determined in the laboratory;
- the permeability coefficient of aquifers was determined using borehole filling;
- laboratory analysis of the sampled soils determined their salt composition;
- the terrain survey delineated promising dam construction sites and conducted a large-scale survey of valleys and floodplains, which enabled the precise determination of the flooded area and the volume of retained water. Topographic survey points were surveyed in the rectangular coordinates of Pulkovo 1942 zone 13N and Pulkovo 1942 zone 12N, depending on the location.
During the terrain survey, 12 potential sites for the construction of a water retention structure (dam) were identified, and a detailed survey of its internal topology was completed.
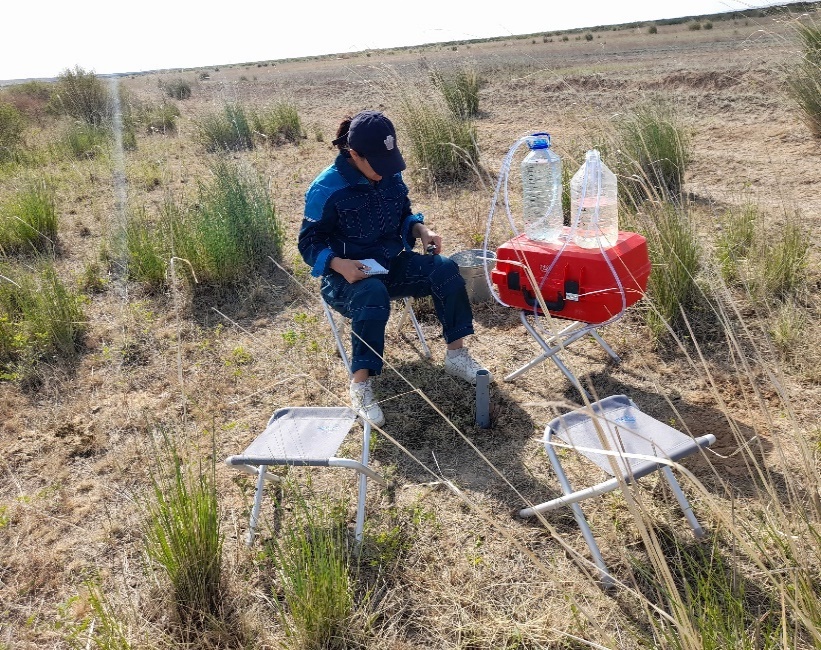
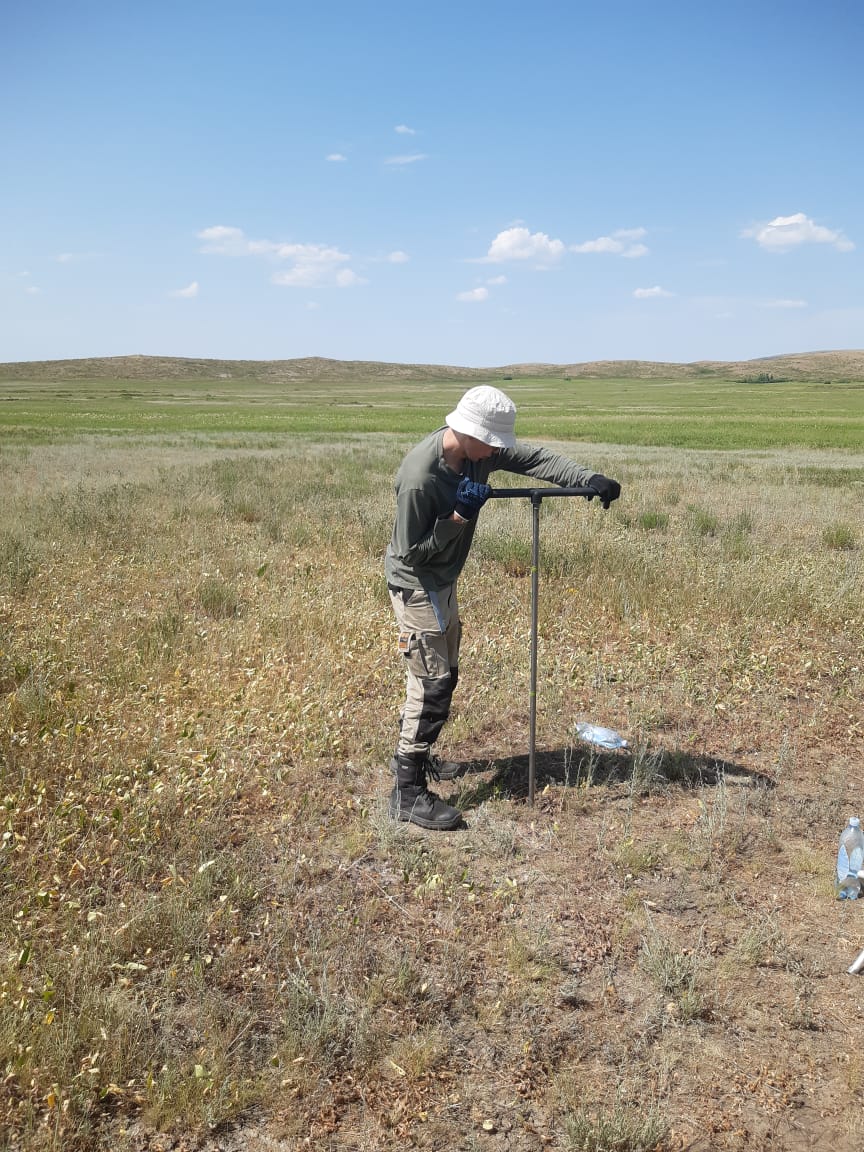
Carrying out pilot filtration works |
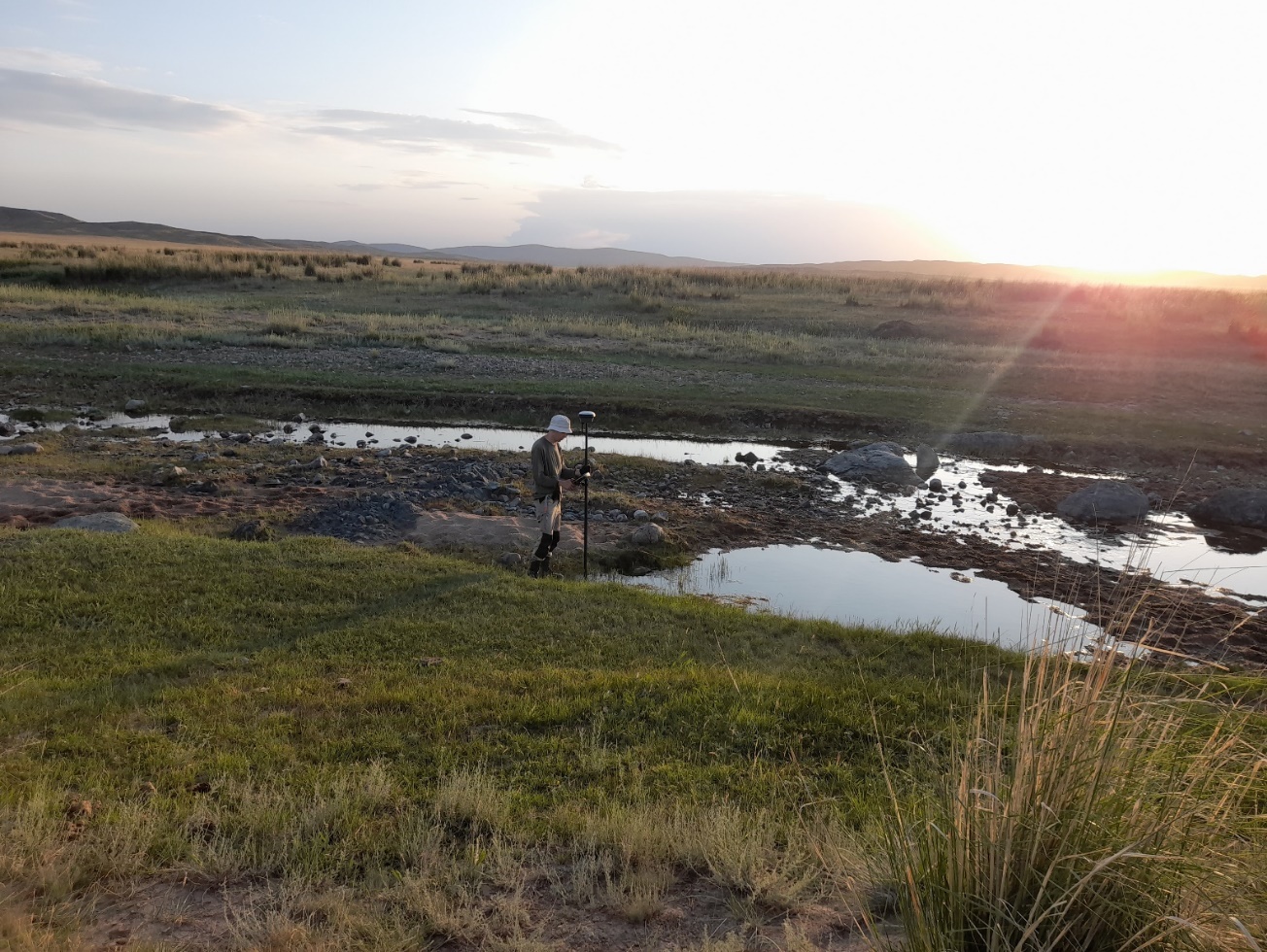
Conducting a topography survey |
The well drilling process |
Photo report on the work carried out |
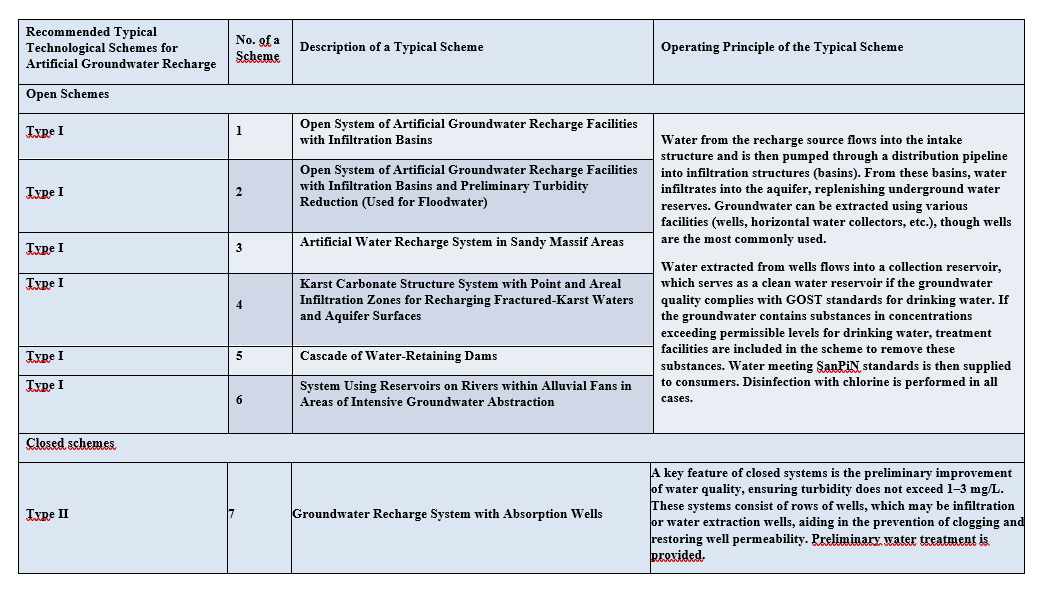
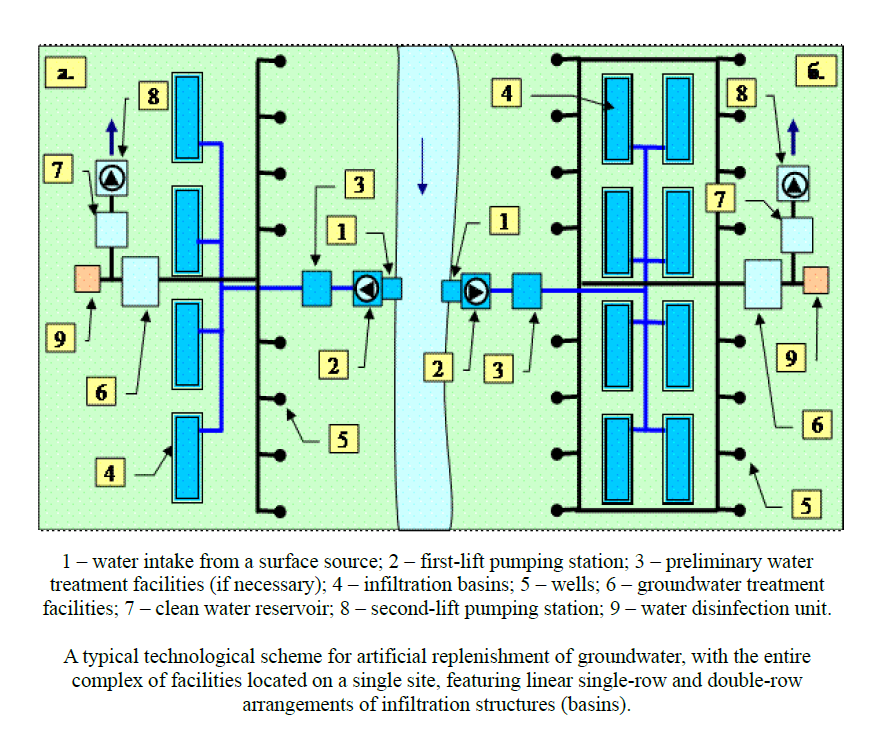
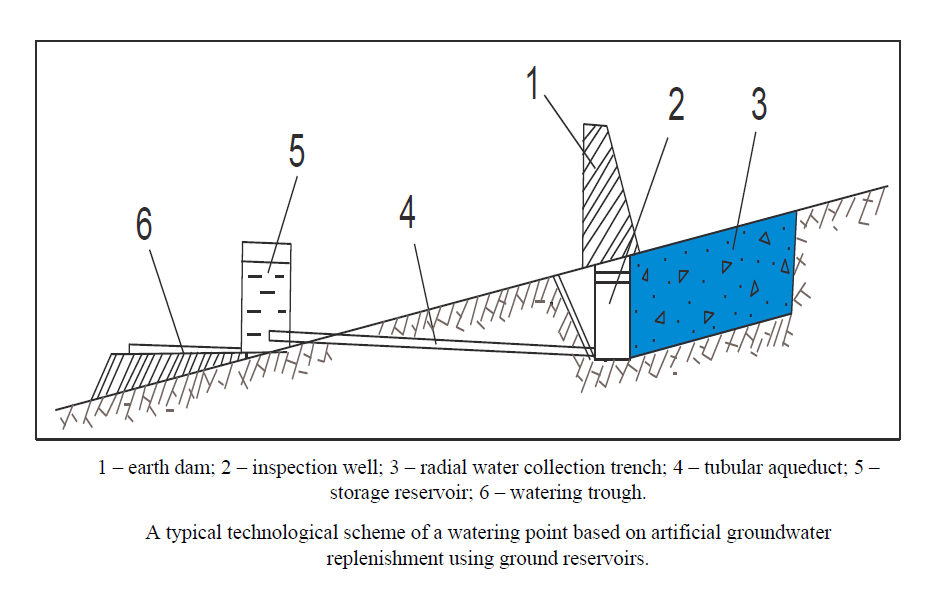
3. Standard process flow diagrams for the MAR were developed, and a preliminary assessment of their potential for use in the Zhanaarka and Shetsky districts of the Ulytau region and certain districts of the Akmola region was conducted. These diagrams are designed for water supply of rural settlements and pasture irrigation.
The schematization is based on the reservoir properties of geological deposits and methods of surface water storage: open and closed types. In the open-type system, recharge occurs through the free filtration of surface water from the Nura, Atasu, Sarysu, Zhaman-Kon, Zhaksy-Kon, and Terenbutak rivers and their tributaries from the basin into the groundwater table. In the closed-type system (Devonian-Carboniferous carbonate structures and Paleozoic intrusive formations in the study area), water is forced into the confined aquifer.
4. Based on a study of the collected cartographic, textual, and tabular materials, paper work was conducted and specialized maps were compiled:
1. General map at a scale of 1:500,000 - for the study area of the Zhanaarka and Shetsky districts of the Ulytau region, as well as individual districts of the Akmola region.
2. Twelve large-scale maps - for individual promising areas.
The maps show perspective aquifers as key elements, characterized by relatively consistent aquifer thicknesses over large areas, high water content in rocks, and good groundwater quality. These include areas of alluvial deposits in river valleys and fractured carbonate rocks.
The most comprehensive information is provided for the aquifer located first from the surface.
Field reconnaissance surveys of 30 sites in the Osakarovsky, Bukhar Zhyrau, Abay, Karkaraly, Aktogay districts of the Karaganda region were conducted, promising sites for the artificial replenishment were identified.
Based on the differentiated area assessment of the studied territory, zoning according to the conditions of the artificial replenishment, which is a scientific justification for the prospects of using the methods of artificial replenishment
Typical technological schemes of artificial replenishment have been developed, the potential for their use in the territory of the Osakarovsky, Bukhar Zhyrau, Abaysky, Karkaraly, Aktogaysky districts of the Karaganda region for water supply of rural settlements and pasture irrigation has been preliminarily assessed.
|
No. |
Full name, education, degree, academic title |
Main place of work, position |
Hirsch index, Researcher ID, ORCID, Scopus Author ID |
|
1 |
Mukhamedzhanov Murat Abikenovich, |
Akhmedsafin Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geoscienc, Chief Researcher of the Laboratory of Regional Hydrogeology and Geoecology |
Hirsch index: 4 |
|
2 |
Jabassov Abay Maratovich, |
Akhmedsafin Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geoscienc, Head of the Groundwater Resources Laboratory |
Researcher ID: |
|
3 |
Onlasynov Zhuldyzbek Alikhanuly, |
Akhmedsafin Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geoscienc, Head of the Laboratory of GIS Technologies and Remote Sensing of the Earth |
Hirsch index 1, |
|
4 |
Rakhimov Timur Aitkalievich |
Akhmedsafin Institute Of Hydrogeology And Environmental Geoscienc, Head of the Laboratory of Regional Hydrogeology and Geoecology, Scientist in the field of hydrogeology and modeling |
Hirsch index: 2, |
|
5 |
Tukeshova Gulziza Esirkepovna |
Akhmedsafin Institute Of Hydrogeology And Environmental Geoscienc, Lead Researcher of the Groundwater Resources Laboratory, Scientist in the field of hydrogeology |
ORCID: 0000-0002-1751-0280 |
|
6 |
Ermenbay Aray Musakyzy |
Akhmedsafin Institute Of Hydrogeology And Environmental Geoscienc, Researcher of the Groundwater Resources Laboratory, Scientist in the field of hydrogeology |
Hirsch index: 3 |
|
7 |
Ereev Danil |
Akhmedsafin Institute Of Hydrogeology And Environmental Geoscienc, Junior Researcher of the Groundwater Resources Laboratory, Scientist in the field of hydrogeology |
ORCID: 0009-0008-6292-6542 |
|
8 |
Zhakibayeva Aigerim Zhanatovna |
Akhmedsafin Institute Of Hydrogeology And Environmental Geoscienc, Junior Researcher of the Groundwater Resources Laboratory, Scientist in the field of hydrogeology |
ORCID: 0000-0002-0226-120 |










